The adoption of artificial intelligence and machine learning represents a fundamental breakthrough for TerrAria, bringing innovation and efficiency in the solutions proposed to the customer. TerrAria has applied machine learning techniques within various algorithms, procedures and applications related to different issues.
Specifically, within the air quality-focused OPERA project, the RIAT+ application uses nonlinear relationships identified by means of artificial neural networks (ANNs) trained to replicate results obtained with deterministic air quality models.
As part of the MASAI project, TerrAria was involved in the development of the deep learning algorithm, applied in the VHR module of the MASAI tool, for the identification of infrastructure damage due to the war in Ukraine from ultra-high resolution satellite imagery.
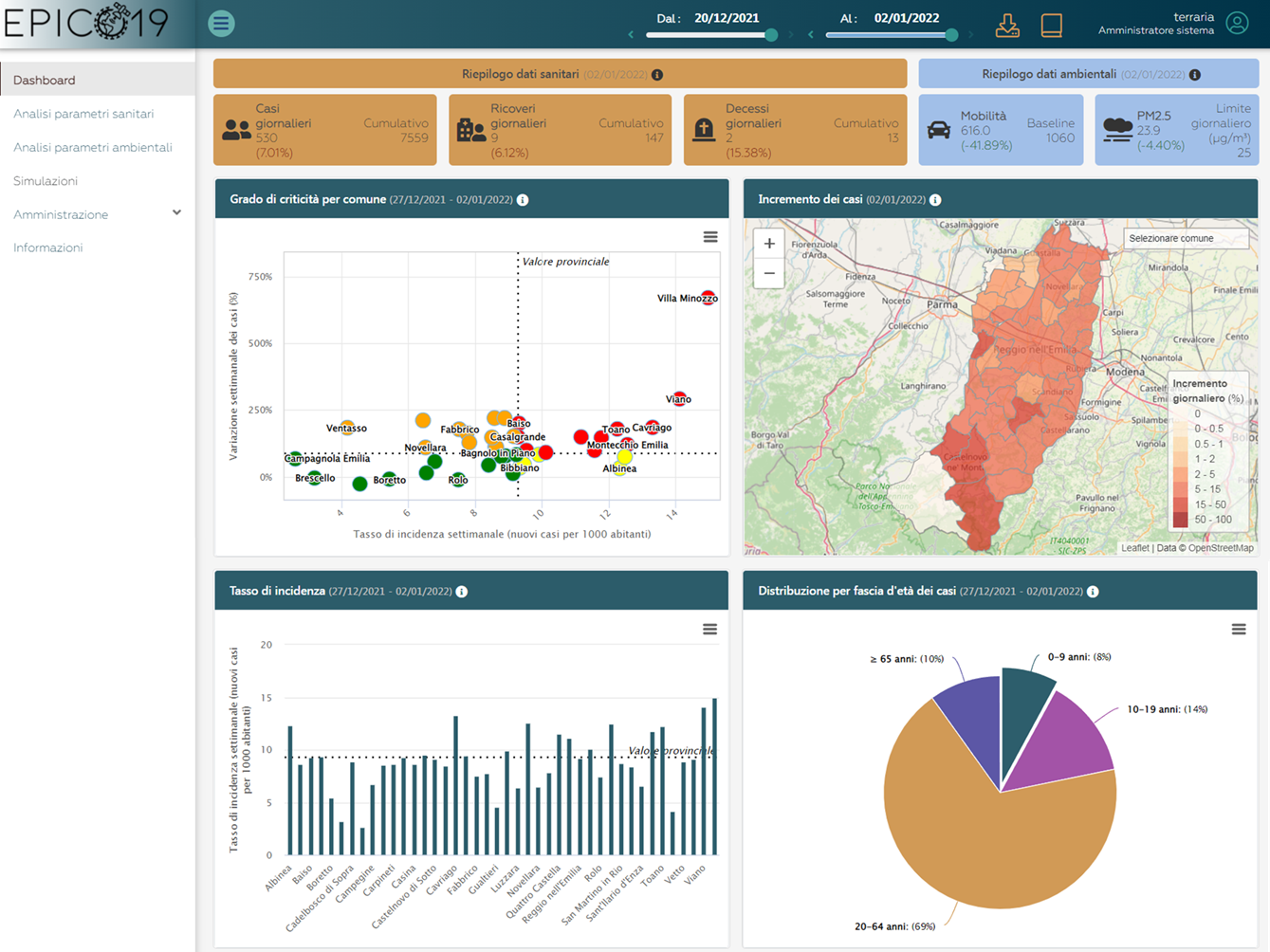
Within the EPICO19 project and its the application, in order to estimate COVID19-related cases and hospitalizations for 7 days and with spatial detail, a deep learning algorithm based on a Convolutional Long Short Term Memory model was employed to take into account the spatial correlation of pandemic spread.

 Research & Development
Research & Development